A home’s foundation is its backbone, supporting the entire structure. When issues arise, they can lead to costly repairs and safety concerns. Home foundation repair isn’t just about fixing cracks; it’s about preserving the integrity of a home. Understanding the signs of foundation problems is crucial for homeowners who want to protect their investment.
From shifting soil to water damage, various factors can compromise a foundation. Early detection and intervention can save homeowners from extensive damage down the line. This article explores common foundation issues, their causes, and effective repair solutions, empowering homeowners to make informed decisions about their properties.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Home Foundation Repair
Home foundation repair addresses structural issues impacting a building’s stability. Foundation problems commonly arise from soil movement, excess moisture, or inadequate drainage. Recognizing these issues early can prevent extensive damage and costly repairs.
Common Signs of Foundation Issues
Homeowners should watch for specific indicators of foundation problems, including:
- Cracks in Walls: Vertical or horizontal cracks may appear in interior or exterior walls.
- Uneven Floors: Sloping or bouncing floors often signal foundation settlement.
- Doors and Windows: Difficulty opening or closing doors and windows may result from shifting frames.
- Water Accumulation: Excessive moisture or standing water near the foundation exacerbates repair needs.
- Gaps: Crevices forming between walls and ceilings suggest structural displacement.
Causes of Foundation Problems
Understanding causes aids in prevention and repair. Common factors include:
- Soil Composition: Expansive soils can shift with moisture changes, affecting stability.
- Poor Drainage: Inadequate drainage systems lead to water pooling, causing erosion.
- Tree Roots: Proximity of large trees may result in root systems that disturb the foundation.
- Foundation Design: Insufficient design or materials may weaken stability from the start.
Repair Methods
Various repair methods are available to restore foundation integrity, including:
- Piering: This method involves installing piers beneath the foundation to support its weight.
- Slabjacking: Slabjacking lifts settled concrete slabs by injecting a polyurethane foam beneath them.
- Wall Bracing: This technique reinforces bowing or leaning walls using steel braces or anchors.
- Drainage Solutions: Installing drainage systems redirects water away from the foundation, preventing further damage.
Ensuring proper foundation repair requires professional assessment. Experienced contractors can identify specific issues and recommend appropriate solutions tailored to the property’s needs.
Common Foundation Problems
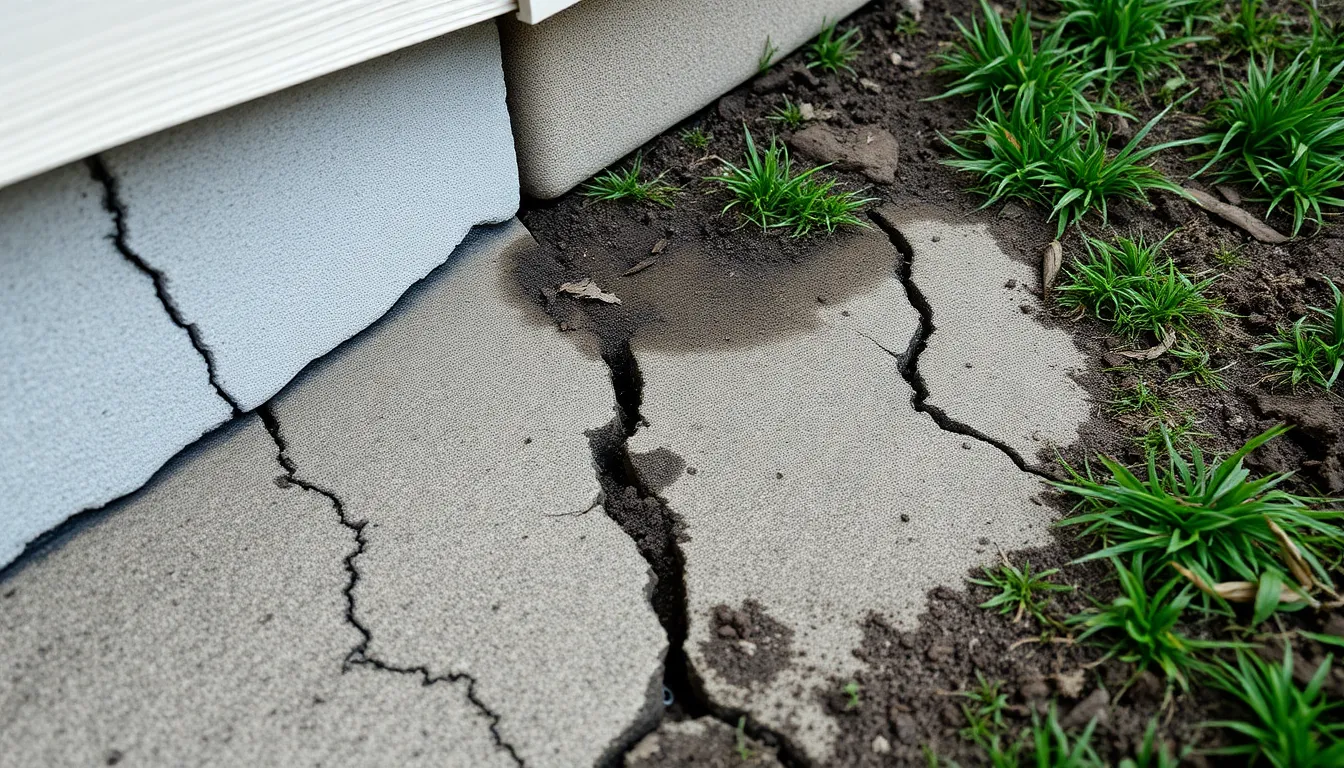
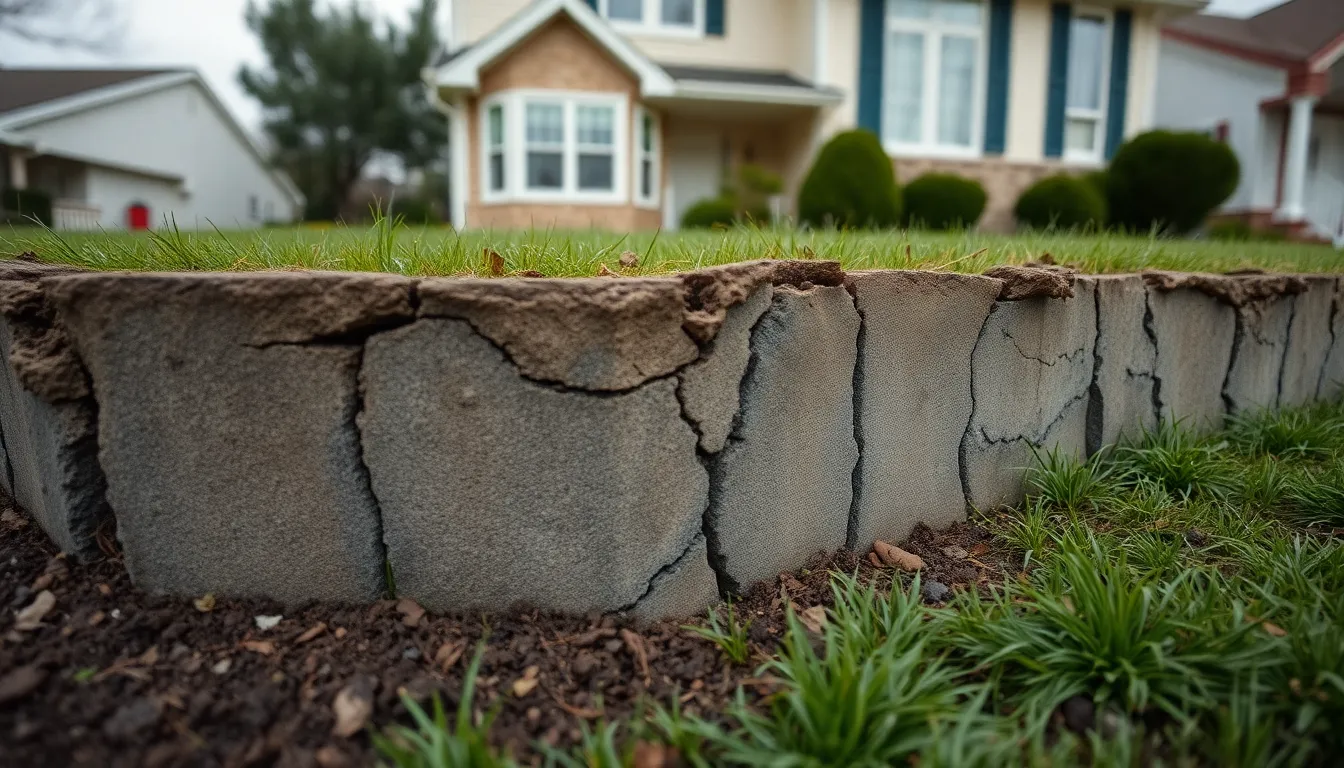


Numerous foundation issues can compromise a home’s integrity. Identifying these problems early can prevent extensive damage and costly repairs.
Cracks in Foundation
Cracks in the foundation signify potential structural problems. Common types of cracks include:
- Vertical Cracks: Often arise from normal settlement or shrinking of concrete. These typically don’t indicate significant issues, but monitoring is essential.
- Horizontal Cracks: Indicate pressure from surrounding soil, often signaling excessive hydrostatic pressure. These can lead to serious structural failure if not addressed promptly.
- Diagonal Cracks: Often a combination of settlement and soil movement. They warrant attention to determine underlying causes.
Homeowners should monitor crack width and length. While small vertical cracks may be manageable, wider or horizontal cracks often require professional assessment.
Uneven Floors
Uneven floors can indicate foundation settlement or heaving. Common causes include:
- Soil Compaction: Improperly compacted soil can lead to settling, causing floors to slope or sag.
- Moisture Issues: Water accumulation near the foundation may erode soil, creating voids that lead to uneven support.
- Tree Roots: Overgrown roots can disrupt soil stability, contributing to uneven flooring.
Homeowners experiencing floor slope or bounce should consult a foundation expert. Addressing the root cause of uneven floors ensures long-term stability and comfort within the home.
Repair Techniques
Home foundation repair employs various techniques tailored to address specific issues. Understanding these methods helps homeowners make informed decisions when dealing with foundation problems.
Piering and Underpinning
Piering and underpinning techniques strengthen a foundation by transferring its load to deeper, more stable soil layers. Piering uses steel or concrete piers, driven into the ground beneath the foundation. This supports the structure and resists settlement shifts. Underpinning involves extending the foundation’s depth or width, often with concrete or steel beams. Both methods provide long-term stability and prevent further movement. Homeowners facing shifting soil or settlement issues find these techniques particularly effective in restoring foundation integrity.
Wall Stabilization
Wall stabilization addresses bowing or leaning walls caused by lateral earth pressure or soil saturation. This method uses steel braces, wall anchors, or carbon fiber strips to stabilize walls, redistributing weight and preventing further movement. Braces attach to the wall and floor, while anchors secure to the ground outside, providing immediate support. Carbon fiber strips offer a less intrusive solution for minor bowing issues. By implementing wall stabilization techniques, homeowners protect their homes from ongoing damage and ensure safety.
Choosing a Foundation Repair Contractor
Selecting a qualified foundation repair contractor is crucial for ensuring effective repairs and long-term stability. Homeowners must evaluate potential contractors based on experience, credentials, and estimates to make informed decisions.
Credentials and Experience
Reviewing relevant credentials assures homeowners of a contractor’s qualifications. Check for licensing and insurance, which protect both the homeowner and the contractor in case of accidents or damages.
Evaluate the contractor’s experience in foundation repair specifically. Contractors with a proven track record in this field often have the expertise to address various issues effectively. Seek contractors with at least five years of experience, as this duration typically indicates a reliable level of skill and knowledge.
Request references and review past projects to gain insights into the contractor’s work quality. Positive feedback from previous clients signals dependable service and successful outcomes. Additionally, check for affiliations with professional organizations, such as the Foundation Repair Association or similar bodies, which often highlight a commitment to industry standards.
Cost Estimates
Obtaining detailed cost estimates is essential for budget management. Contractors should provide comprehensive estimates that outline materials, labor, and any additional expenses. Homeowners must compare estimates from multiple contractors to identify reasonable pricing while considering the scope of work.
Estimates should also include a breakdown of costs associated with specific repair methods, such as piering or wall stabilization. This clarity helps homeowners understand where funds will go and informs their selection process.
Inquire about warranty options. Reliable contractors often back their work with warranties or guarantees. A solid warranty not only reflects confidence in the quality of repairs but also provides peace of mind for the homeowner regarding future issues.
By assessing credentials, experience, and cost estimates, homeowners secure the right foundation repair contractor, ultimately ensuring effective solutions for their home’s stability.
Preventative Measures for Foundation Longevity
Implementing preventative measures can significantly extend the lifespan of a home’s foundation. Proper drainage and soil maintenance play crucial roles in maintaining foundation integrity.
Drainage Solutions
Effective drainage solutions prevent water accumulation around the foundation, reducing the risk of soil saturation and resulting damage. Homeowners should:
- Install Gutters: Ensure gutters direct rainwater away from the foundation. Downspouts should extend at least five feet from the base of the house.
- Grade Landscaping: Landscape grading should slope away from the foundation, allowing water to flow away from the home.
- Use French Drains: French drains help manage excess water by channeling it away from the foundation, especially in areas prone to pooling.
- Incorporate Sump Pumps: In high-risk areas, sump pumps can be used to remove accumulated water from basements or crawl spaces, minimizing moisture levels.
Soil Maintenance
Proper soil maintenance enhances foundation stability by mitigating issues caused by shifting or expanding soils. Homeowners can:
- Avoid Soil Compaction: Heavy equipment or excessive foot traffic should be minimized around the foundation area to prevent soil compaction.
- Mulch and Fertilize: Applying mulch and appropriate fertilizers can help retain soil moisture levels, preventing drastic fluctuations that affect foundation stability.
- Water Regularly: Regular watering during dry seasons keeps soil in a balanced state, reducing the risk of shrinkage that could lead to foundation problems.
- Monitor Tree and Root Growth: Roots from nearby trees should be monitored, as they can draw moisture from the soil or cause physical damage to the foundation. Consider removing or relocating any trees too close to the home.
By adopting these drainage and soil maintenance strategies, homeowners can enhance their foundation’s longevity and safeguard their property against potential issues.