In the world of software development, an application architecture diagram is like a treasure map. It guides developers through the complex landscape of code, servers, and user interactions, ensuring they don’t get lost in the digital jungle. Think of it as the blueprint for a skyscraper—without it, you might end up with a very fancy treehouse instead.
Table of Contents
ToggleImportance Of Application Architecture Diagram
Application architecture diagrams play a crucial role in the software development process. These diagrams create a clear structure that guides developers in building applications efficiently.
Understanding System Components
Understanding system components is vital for project success. Each component, whether a database, server, or user interface, interacts within the overall ecosystem. Developers identify these components to determine how they communicate with one another. This analysis helps visualize dependencies among services, leading to better integration strategies. Clear identification of components also aids in pinpointing potential performance bottlenecks. With this framework, teams can ensure all necessary elements fit seamlessly together.
Visual Representation Benefits
Visual representation benefits include enhanced clarity and improved communication among stakeholders. Diagrams allow technical and non-technical team members to grasp complex architecture easily. Stakeholders can visualize relationships and data flow, enabling informed decision-making. Moreover, diagrams serve as reference points throughout the project’s lifecycle. Updates become easier when each component’s function is clearly defined. Clear visuals promote collaboration, ensuring all team members share a common understanding of the architecture. With shared knowledge, teams can address challenges more effectively.
Key Elements Of Application Architecture Diagram
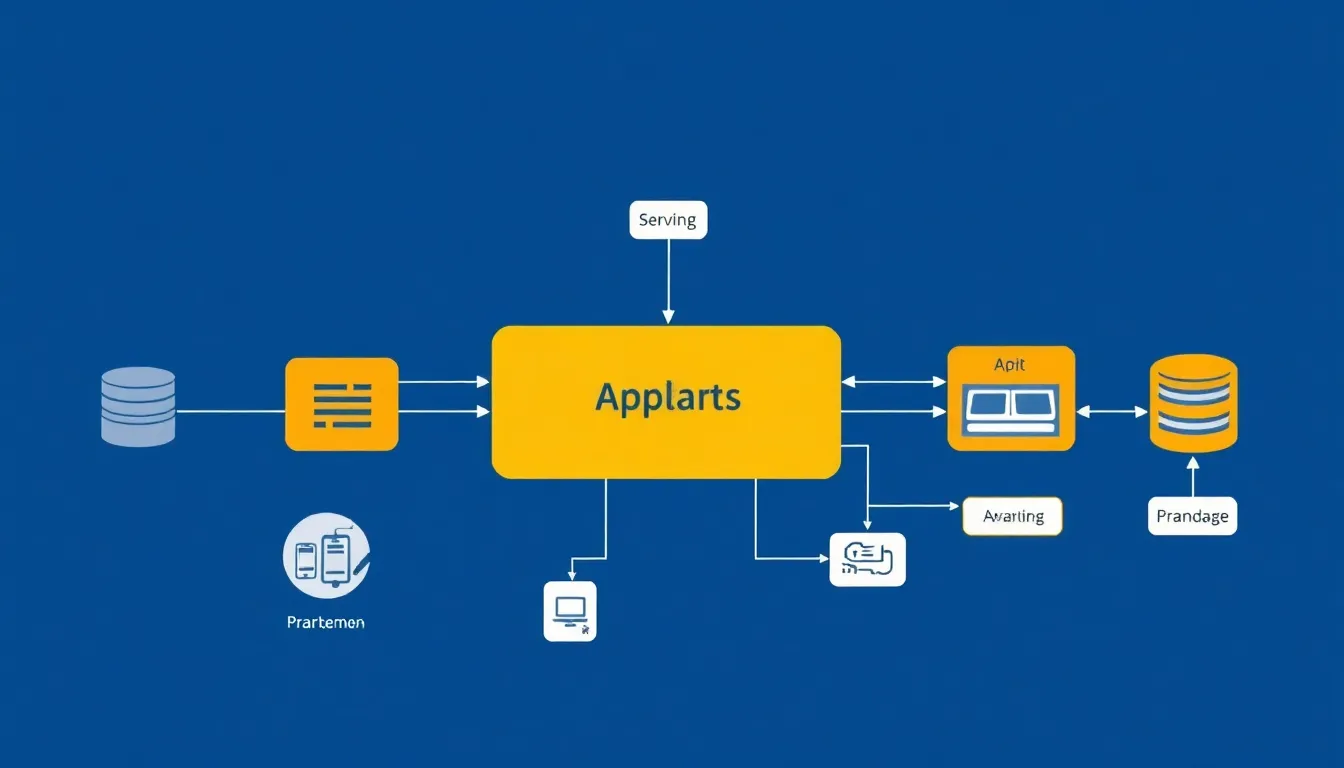
Application architecture diagrams consist of critical components that provide insights into how software applications operate. Understanding these elements proves essential for developers in creating effective systems.
Components Overview
Diagrams typically include databases, servers, user interfaces, and APIs. Each element serves a unique role in the application ecosystem. Databases manage data storage and retrieval, while servers handle requests and processing. User interfaces interact with end-users, providing a means for input and output. APIs facilitate communication between different application parts, enabling seamless integration of services. Properly representing these components illustrates how they contribute to the overall architecture, ensuring clarity and coherence.
Interactions And Relationships
Understanding interactions among components is vital for identifying dependencies and workflows. Each component exchanges data, which influences performance and functionality. For instance, APIs connect front-end interfaces with back-end servers, creating a dynamic workflow. Databases rely on efficient queries from servers, impacting user experience. Visualizing these relationships enhances the understanding of how changes in one area affect the entire system. By mapping interactions, developers anticipate potential bottlenecks, optimizing performance and productivity.
Types Of Application Architecture Diagrams
Application architecture diagrams come in various types, each catering to distinct development needs. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right approach for a project.
Layered Architecture
Layered architecture focuses on separating the application into distinct layers. Each layer handles specific responsibilities, enhancing organization and maintainability. The layers typically include presentation, business logic, and data access. This structure enables developers to modify one layer without impacting others, promoting flexibility. Adding new features often becomes more straightforward within this framework. An example includes a web application where users interact through the presentation layer, while business rules operate in the logic layer, and data is stored in the database layer. Clear visualization of these layers aids in comprehending the application’s flow and interactions.
Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture emphasizes building applications as a collection of smaller, independent services. Each service is responsible for a specific functionality, allowing for modular development. Developers can deploy, scale, and manage each service independently, improving resilience and efficiency. Communication between services typically occurs via REST APIs or message brokers, enabling seamless integration. This architecture supports parallel development by different teams, accelerating delivery timelines. An example consists of an e-commerce platform with separate services for user accounts, product management, and payment processing. Diagrams illustrate service interactions and data flow, which assist in troubleshooting and optimizing the overall system.
Best Practices For Creating Application Architecture Diagrams
Application architecture diagrams should emphasize clarity and simplicity while maintaining essential details. Clear diagrams promote understanding and help avoid confusion among team members. Simplicity enhances readability, making the diagrams accessible to both technical and non-technical stakeholders. Using concise labels and straightforward symbols assists in conveying the information effectively. Incorporating ample white space ensures that each component stands out, allowing viewers to focus easily on each part.
Consistency in notation across diagrams fosters a shared language among developers. Defining and adhering to a set of symbols and terminology minimizes misunderstandings. For instance, using standard icons for servers, databases, and APIs reinforces familiarity among team members. Maintaining consistent color schemes helps differentiate between various components and their functions. Additionally, establishing naming conventions streamlines communication, which is critical for collaborative work. By prioritizing consistency, teams can improve workflow and enhance overall project efficiency.
Application architecture diagrams are indispensable tools in modern software development. They not only provide clarity and structure but also enhance collaboration among team members. By visualizing components and their interactions, these diagrams empower developers to make informed decisions and optimize performance.
The importance of simplicity and consistency in these diagrams cannot be overstated. Clear visuals foster understanding across technical and non-technical stakeholders, minimizing confusion and streamlining communication. As projects evolve, these diagrams serve as vital reference points, ensuring that teams remain aligned and focused on their goals. Embracing these best practices will undoubtedly lead to more efficient and successful software development endeavors.