Imagine walking through a city where the buildings reach for the heavens and the gardens are so lush they could make even the most seasoned botanist weep with joy. That’s Babylon for you, the ancient wonder that not only captured hearts but also set the gold standard for architecture. With its grand ziggurats and intricate palaces, Babylonian architecture was like the original Instagram filter—making everything look better and more impressive.
But it wasn’t just about aesthetics; these structures were engineering marvels that stood the test of time. From the famed Hanging Gardens to the towering Ishtar Gate, each design element tells a story of ambition, innovation, and a sprinkle of divine inspiration. Dive into the fascinating world of Babylonian architecture and discover how these ancient builders laid the groundwork for modern design, proving that sometimes, the past really does have a few tricks up its sleeve.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Babylonian Architecture
Babylonian architecture displays remarkable ingenuity and creativity. It features large platforms, extensive use of mudbrick, and decorative ceramics that characterized the region. Structures often served dual purposes, combining religious significance with administrative functions. Temples, such as the ziggurat, dominated cityscapes, functioning as both a place of worship and a symbol of power.
The Ishtar Gate represents one of the most iconic examples, adorned with vibrant glazed tiles depicting animals. This entrance to the city highlighted the importance of aesthetics alongside functionality. The combination of practical design and intricate artistry enabled the Babylonians to create structures that were not only enduring but also visually striking.
Urban planning in Babylon also demonstrated advanced understanding. City layouts incorporated straight streets and public spaces, facilitating movement and enhancing daily life. Walls surrounding cities featured monumental gates, reinforcing defense while impressing visitors with their grandeur.
Significant advancements in engineering led to the creation of vast irrigation systems supporting agriculture. These developments contributed to the prosperity of Babylon, resulting in a flourishing society capable of complex architectural projects. The Hanging Gardens, although their existence remains debated, epitomize the splendor attributed to Babylonian craftsmanship.
Overall, Babylonian architecture symbolizes a blend of functionality, artistry, and innovation. Its enduring influence continues to resonate in modern architectural practices, bridging the ancient with contemporary design principles. Through examining these monumental works, a deeper appreciation for the sophistication of Babylonian achievements emerges.
Key Features of Babylonian Architecture
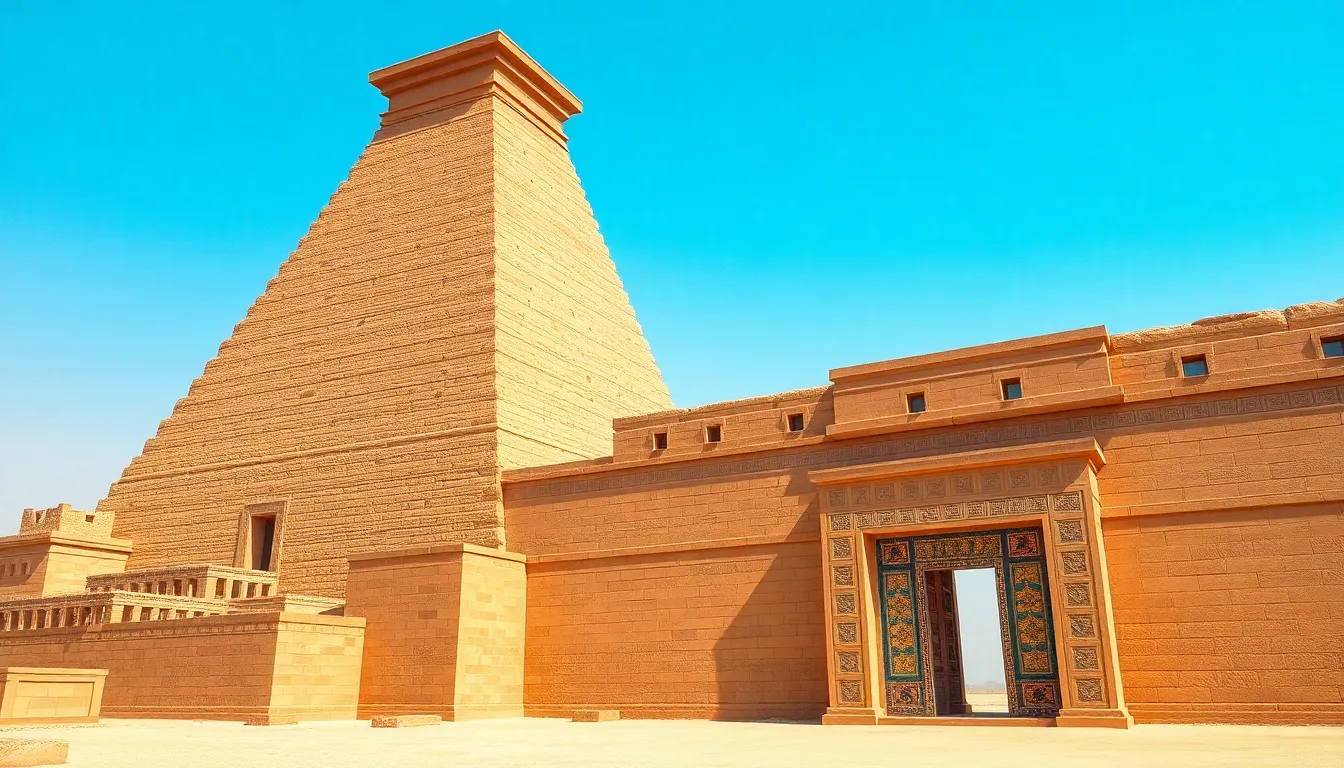

Babylonian architecture is marked by distinctive characteristics that showcase ancient ingenuity. Key features include the materials used and the diverse architectural styles that emerged.
Use of Materials
Mudbrick dominated construction in Babylon due to its abundance and insulation properties. This material provided structural integrity while allowing for intricate designs. Stone was also utilized for important structures like temples and palaces. Decorative ceramics enriched facades, exemplifying the artistry of Babylonian craftsmen. These materials contributed to the durability of structures, many of which withstand time. By combining various elements, Babylonian architects achieved remarkable consistency in their designs.
Architectural Styles
Ziggurats served as the pinnacle of Babylonian architectural style, featuring tiered levels and grand staircases. Their design emphasized religious importance, often functioning as temples to deities. Arched gateways, like the Ishtar Gate, reflected advancements in engineering while adding aesthetic value. Walls adorned with vibrant tiles illustrated the blend of color and form. Square and rectangular layouts defined urban planning, establishing organized city spaces. Each style exemplified a fusion of form and function rooted in the culture and beliefs of the Babylonians.
Notable Structures in Babylonian Architecture
Babylonian architecture features remarkable structures that reflect its cultural significance and engineering prowess. Two of the most notable examples include the Hanging Gardens and the Ishtar Gate.
The Hanging Gardens
The Hanging Gardens represent an ancient marvel, often described as one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. They reportedly consisted of tiered gardens filled with various trees, flowers, and plants. Scholars believe these gardens might have been constructed using a series of terraces, showcasing advanced irrigation techniques that ensured lush greenery. Although their exact location remains uncertain, they symbolize the ingenuity and creativity inherent in Babylonian design.
The Ishtar Gate
The Ishtar Gate stands as a stunning example of Babylonian artistry and engineering. Adorned with vibrant blue glazed bricks and intricate reliefs, it served as a ceremonial entrance to the city. The gate featured depictions of dragons and bulls, representing the gods Marduk and Adad. Built during the reign of King Nebuchadnezzar II, the Ishtar Gate highlights the importance of religious and political symbolism in Babylonian architecture. Its construction demonstrated advanced craftsmanship and left a lasting legacy in the history of architecture.
Influence on Future Architectures
Babylonian architecture has profoundly influenced various architectural styles across different cultures and eras. Its innovations in construction techniques, particularly the extensive use of mudbrick, set a precedent for subsequent builders. Builders in ancient Rome adopted similar brickwork practices, demonstrating the adaptability of these techniques.
The iconic ziggurat structures, characterized by their tiered levels, inspired pyramid-like designs in Mesoamerican civilizations. Many architects recognized the symbolic significance of height in architecture, leading to the creation of monumental religious structures. These ziggurats informed the design of later temples and religious buildings throughout history.
Urban planning concepts from Babylon, such as organized street layouts and the inclusion of public spaces, shaped city designs in subsequent civilizations. Influencers in the Renaissance found inspiration in Babylonian urban organization, integrating principles of order and functionality in their own city plans. Notable examples include the planned towns of Italy, where rectilinear streets and squares came to prominence.
Artistic aspects of Babylonian architecture also resonated with later artists and architects. The use of glazed tiles seen in the Ishtar Gate served as a significant reference point for Islamic architecture, leading to the development of intricate tilework. Craftsmen in various cultures sought to replicate the vibrancy and craftsmanship of Babylonian designs.
Engineering advancements related to irrigation systems had lasting importance. Agricultural techniques pioneered by the Babylonians laid groundwork for sophisticated hydraulic systems in medieval European architecture. Through these engineering feats, the understanding of water management in urban environments expanded.
Overall, the legacy of Babylonian architecture continues to inspire and inform modern architecture, establishing a foundation that architects build upon today. Its blend of functionality, artistry, and innovative engineering remains a touchstone for contemporary architectural practices.
Babylonian architecture stands as a testament to human creativity and engineering prowess. The remarkable structures of ancient Babylon not only shaped their environment but also laid the groundwork for future architectural endeavors. Their innovative use of materials and design principles continues to inspire architects and builders today.
The legacy of Babylonian architecture is evident in modern practices, reminding us of the importance of blending aesthetics with functionality. As we explore and appreciate these ancient marvels, we gain valuable insights into the evolution of architecture and the timelessness of great design.