When it comes to industrial building construction, it’s not just about pouring concrete and raising walls. It’s about creating spaces where innovation meets functionality, where the magic of productivity happens. Think of it as crafting a giant playground for grown-ups—except instead of swings and slides, there are assembly lines and storage facilities.
In today’s fast-paced world, the demand for robust industrial structures is skyrocketing. Companies need spaces that not only meet their operational needs but also adapt to future growth. So whether you’re planning a new factory or expanding an existing warehouse, understanding the ins and outs of industrial construction can make all the difference. Get ready to dive into the nuts and bolts of this fascinating industry, where every beam and bolt tells a story of progress and potential.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of Industrial Building Construction
Industrial building construction encompasses various elements that contribute to creating efficient and effective facilities. This sector includes manufacturing plants, warehouses, distribution centers, and specialized facilities designed for industry-specific operations. Understanding the fundamental aspects of industrial construction leads to enhanced project outcomes.
Design plays a crucial role in this area. Efficient layouts facilitate workflow and enhance productivity. Architects and engineers collaborate to create spaces that accommodate heavy machinery, storage requirements, and safety considerations.
Materials selection significantly impacts durability and functional performance. Steel and concrete dominate the industry for their strength and longevity. Every project benefits from choosing materials that withstand environmental challenges while meeting operational demands.
Construction techniques have evolved to align with technology and efficiency. Prefabrication and modular building approaches reduce construction timelines and costs. These methods enhance construction flexibility and allow for rapid responses to market changes.
Regulations and safety standards guide industrial building construction. Compliance with local codes, environmental regulations, and safety protocols ensures that projects adhere to legal and operational guidelines. This adherence fosters safer work environments and promotes sustainable practices.
Project management emerges as a pivotal component. Effective planning, coordination, and execution mitigate risks and optimize resource allocation. Utilizing project management software facilitates real-time tracking of progress, costs, and timelines.
Investment in industrial construction remains strong. Companies increasingly prioritize modern facilities that support current needs and future growth. This trend reflects the dynamic nature of industrial operations, driven by advancements in technology and market demands.
Through a combination of strategic planning, innovative design, and stringent compliance, industrial building construction shapes the infrastructure needed for modern industry.
Key Components of Industrial Buildings
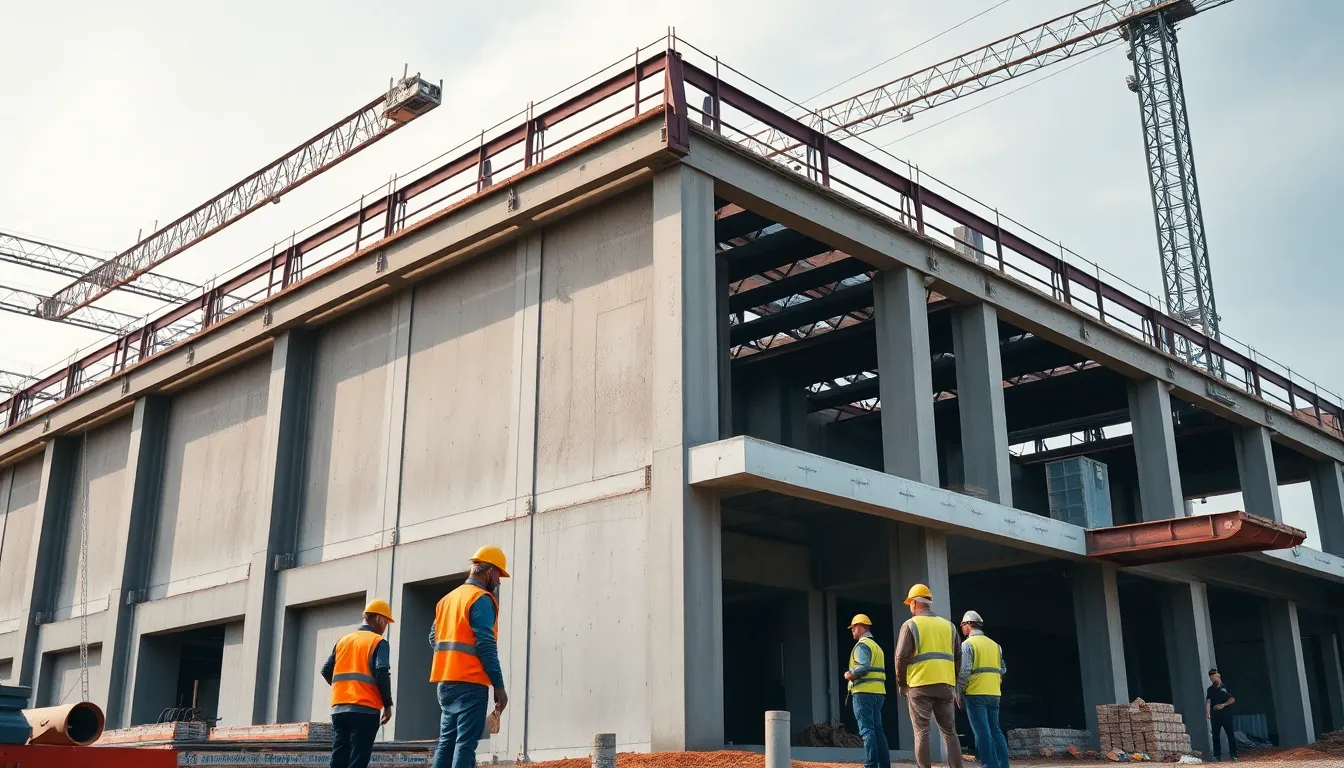

Industrial buildings consist of several critical components that ensure functionality and durability. Each component contributes to the overall efficiency of operations.
Structural Elements
Structural elements form the backbone of industrial buildings. They typically include beams, columns, and slabs, providing support and stability. Steel frames often dominate due to their strength and resistance to environmental factors. Concrete elements, utilized in foundations and walls, offer durability and load-bearing capabilities. Roof systems, such as trusses, enable the creation of large unobstructed spaces, facilitating the movement of machinery and materials. Insulation and weatherproofing also enhance energy efficiency, reducing operational costs over time.
Electrical and Plumbing Systems
Electrical and plumbing systems play vital roles in industrial buildings. Electrical systems must support heavy machinery and provide sufficient lighting in workspaces. This involves designing layouts that deliver power efficiently while ensuring safety compliance. Additionally, specialized wiring often supports automation and control systems. Plumbing systems address both sanitation and process requirements. They include water supply lines, drainage systems, and specialized piping for certain processes. These must also comply with health standards, prioritizing worker safety and operational efficiency.
Innovative Techniques in Industrial Building Construction
Innovative techniques drive efficiency and effectiveness in industrial building construction, enabling projects to meet modern demands.
Prefabrication and Modular Construction
Prefabrication streamlines the construction process by assembling components off-site. This method reduces on-site labor and speeds up project timelines. Modular construction involves creating entire sections of a building in controlled environments. These constructed modules can be rapidly transported and assembled on-site, minimizing disruption. Companies adopting these techniques often report significant cost savings and shorter completion periods. The precision of factory production also enhances overall quality, ensuring higher consistency in materials and finishes.
Sustainable Building Practices
Sustainable building practices focus on minimizing environmental impact while maximizing energy efficiency. Utilizing recycled materials in construction reduces waste and promotes resource conservation. Incorporating energy-efficient systems, such as solar panels and high-performance insulation, fosters lower operational costs. Water-saving fixtures and green roofing systems improve overall sustainability, enhancing indoor air quality. Many businesses adopting these practices benefit from reduced energy bills and enhanced corporate reputation, positioning themselves as environmentally responsible leaders in the industry.
Challenges in Industrial Building Construction
Industrial building construction presents various challenges that can impact project success. Recognizing these obstacles is vital for effective planning and execution.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance poses significant challenges in industrial building construction. Stricter local, state, and federal regulations ensure safety and environmental standards are met. Maintaining compliance often requires extensive documentation and adherence to specific guidelines. Industry stakeholders must keep up with changes in regulations to avoid penalties. Non-compliance can lead to costly delays, litigation, and even project shutdowns. Consulting experienced legal and regulatory professionals during the planning phase helps navigate complex requirements. Adapting to these challenges not only ensures a smoother construction process but also guarantees safer work environments.
Budget Constraints
Budget constraints often limit the resources available for industrial building projects. Stakeholders face pressure to deliver high-quality facilities within restricted financial parameters. Unexpected costs can arise from delays, regulatory changes, or material price fluctuations. Developing a realistic budget that includes contingency plans for unforeseen expenses is crucial. Prioritizing essential elements of the construction like reliable materials and skilled labor optimizes financial resources. Effective project management coordinates spending and aligns it with overall objectives. Investing time in thorough financial planning mitigates risks and supports the project’s success despite budget limitations.
Future Trends in Industrial Building Construction
Emerging trends in industrial building construction focus on innovation and efficiency. These advancements actively shape the future of the industry.
Technological Advancements
Automation processes significantly enhance productivity within industrial facilities. Robotics in construction assists with tasks like masonry and assembly, streamlining workflows and reducing labor costs. Building Information Modeling (BIM) supports better design accuracy and project management. Smart buildings incorporate IoT technology, enabling real-time monitoring of systems such as HVAC and energy usage. Virtual reality augments design processes, allowing stakeholders to visualize projects before implementation. These technological innovations facilitate increased collaboration among teams and reduce construction delays.
Market Demand
The demand for industrial buildings continuously evolves with market changes. E-commerce growth drives the need for more warehouses and distribution centers. Sustainable practices also gain traction as companies prioritize eco-friendly developments. Preferences lean toward facilities that support efficient logistics and rapid order fulfillment. Industrial spaces that can adapt to changing technologies draw investor interest. Flexibility in design accommodates shifting operational requirements. Therefore, meeting these demands positions projects for long-term success in the competitive landscape.
The landscape of industrial building construction is evolving rapidly. As businesses strive to create efficient and adaptable facilities, the focus on innovative techniques and sustainable practices is more important than ever. Embracing advancements like prefabrication and smart technologies not only enhances productivity but also positions companies as leaders in sustainability.
Navigating regulatory challenges and budget constraints requires careful planning and strategic decision-making. By prioritizing essential elements and ensuring compliance, businesses can mitigate risks and maximize their investment. The future of industrial construction is bright, driven by a commitment to quality, efficiency, and adaptability. This dynamic sector will continue to shape the infrastructure necessary for modern industry, meeting the demands of a changing marketplace.